|
(Picture
Source)
By far the largest carnivore in its
environment, Tyrannosaurus rex
may have been an apex predator, preying upon
hadrosaurs and
ceratopsians,
although some experts have suggested it was primarily a scavenger. The
debate over Tyrannosaurus
as apex predator or scavenger is among the longest running debates in
paleontology.
More than 30 specimens of
Tyrannosaurus rex
have been identified, some of which are nearly complete skeletons. Soft
tissue and proteins have been reported in at least one of these specimens.
The abundance of fossil material has allowed significant research into many
aspects of its biology, including life history and biomechanics. The feeding
habits, physiology and potential speed of
Tyrannosaurus rex are a few subjects of debate.
Its taxonomy is also controversial, with some scientists considering
Tarbosaurus bataar from
Asia to represent a second species of
Tyrannosaurus and
others maintaining
Tarbosaurus as a
separate genus. Several other genera of North American tyrannosaurids have
also been
synonymized with
Tyrannosaurus.
Description
Tyrannosaurus rex
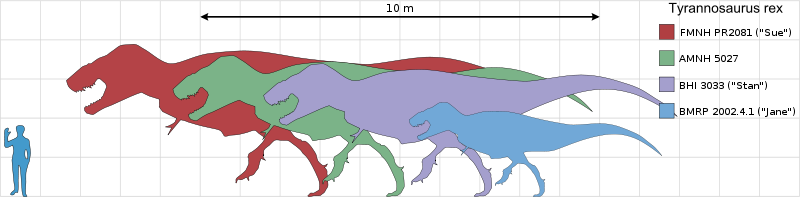
was one of the largest land carnivores of all time; the largest complete
specimen, FMNH PR2081 ("Sue"),
measured 42 feet (12.8 m) long, and was 13 feet (4.0 m) tall at the
hips. Mass estimates have varied widely over the years, from more than
7.9 short tons (15,800 lbs) to less than 5 tons (10,000 lbs), with most modern estimates ranging between
6.0 and 7.5 tons
(5.4 and 6.8 metric tons). Although
Tyrannosaurus rex was larger than the well known
Jurassic theropod
Allosaurus, it was
slightly smaller than some other Cretaceous carnivores, such as
Spinosaurus and
Giganotosaurus.
The neck of
Tyrannosaurus rex formed a
natural S-shaped curve like that of other theropods, but was short and
muscular to support the massive head. The forelimbs had only two clawed
fingers, along with an additional small
metacarpal representing
the remnant of a third digit. In contrast the hind limbs were among the
longest in proportion to body size of any theropod. The tail was heavy and
long, sometimes containing over forty vertebrae, in order to balance the
massive head and torso. To compensate for the immense bulk of the animal,
many bones throughout the skeleton were hollow, reducing its weight without
significant loss of strength.
The largest known
Tyrannosaurus rex skulls
measure up to 5 feet (1.5 m) in length. Large
fenestrae (openings) in the skull reduced weight
and provided areas for muscle attachment, as in all carnivorous theropods.
But in other respects Tyrannosaurus’
skull was significantly different from those of large non-tyrannosauroid
theropods. It was extremely wide at the rear but had a narrow snout,
allowing unusually good
binocular vision. The
skull bones were massive and the
nasals
and some other bones were fused, preventing movement between them; but many
were pneumatized (contained a "honeycomb" of tiny air spaces) which may have
made the bones more flexible as well as lighter. These and other
skull-strengthening features are part of the tyrannosaurid trend towards an
increasingly powerful bite, which easily surpassed that of all non-tyrannosaurids.
The tip of the upper jaw was U-shaped (most non-tyrannosauroid carnivores
had V-shaped upper jaws), which increased the amount of tissue and bone a
tyrannosaur could rip out with one bite, although it also increased the
stresses on the front teeth.
The teeth of
Tyrannosaurus rex
displayed marked
heterodonty
(differences in shape). The premaxillary teeth at the front of the upper jaw
were closely packed, D-shaped in cross-section, had reinforcing ridges on
the rear surface, were incisiform (their tips were chisel-like blades) and
curved backwards. The D-shaped cross-section, reinforcing ridges and
backwards curve reduced the risk that the teeth would snap when
Tyrannosaurus bit and pulled. The remaining
teeth were robust, like "lethal bananas" rather than daggers; more widely
spaced and also had reinforcing ridges. Those in the upper jaw were larger
than those in all but the rear of the lower jaw. The largest found so far is
estimated to have been 12 inches long (30 cm) including the root when
the animal was alive, making it the largest tooth of any carnivorous
dinosaur.
Tyrannosaurus
is the
type genus of the
superfamily Tyrannosauroidea, the family
Tyrannosauridae, and the subfamily Tyrannosaurinae; in other words it is the
standard by which paleontologists decide whether to include other species in
the same group. Other members of the tyrannosaurine subfamily include the
North American
Daspletosaurus and the
Asian Tarbosaurus,
both of which have occasionally been synonymized with
Tyrannosaurus.
Tyrannosaurids were once commonly thought to be descendants of earlier large
theropods such as
megalosaurs and
carnosaurs, although
more recently they were reclassified with the generally smaller
coelurosaurs.
Notable Specimens
Sue Hendrickson,
amateur
paleontologist, discovered the most complete (approximately 85%) and, until
2001, the largest,
Tyrannosaurus
fossil skeleton known in the
Hell Creek Formation
near
Faith, South Dakota, on
12 August 1990. This
Tyrannosaurus,
nicknamed "Sue"
in her honor, was the object of a legal battle over its ownership. In 1997
this was settled in favor of Maurice Williams, the original land owner. The
fossil collection was purchased by the
Field Museum of Natural History
at auction for
7.6 million (U.S. dollars), making it the most expensive dinosaur skeleton to date. From
1998 to 1999 Field Museum of Natural History workers spent over 25,000 man-hours taking the rock off each of the
bones. The bones were then shipped off to New Jersey where the mount was
made. The finished mount was then taken apart, and along with the bones,
shipped back to Chicago for the final assembly. The mounted skeleton opened
to the public on May 17, 2000 in the great hall (Stanley Field Hall) at the Field Museum of Natural History.
A study of this specimen's fossilized bones showed that "Sue" reached full
size at age 19 and died at age 28, the longest any tyrannosaur is known to
have lived. Early speculation that Sue may have died from a bite to the back
of the head was not confirmed. Though subsequent study showed many
pathologies in the skeleton, no bite marks were found. Damage to the back of
the skull may have been caused by post-mortem trampling. Recent speculation
indicates that "Sue" may have died of starvation after contracting a
parasitic infection from eating diseased meat; the resulting infection would
have caused inflammation in the throat, ultimately leading "Sue" to starve
because she could no longer swallow food. This hypothesis is substantiated
by smooth-edged holes in her skull which are similar to those caused in
modern-day birds that contract the same parasite.
Another
Tyrannosaurus, nicknamed
"Stan", in honor of amateur paleontologist Stan Sacrison, was found in the
Hell Creek Formation near
Buffalo, South Dakota,
in the spring of 1987. After 30,000 man-hours of digging and preparing, a
65% complete skeleton emerged. Stan is currently on display in the Black
Hills Museum of Natural History Exhibit in
Hill City, South Dakota,
after an extensive world tour. This tyrannosaur, too, was found to have many
bone pathologies, including broken and healed ribs, a broken (and healed)
neck and a spectacular hole in the back of its head, about the size of a
Tyrannosaurus tooth. Both "Stan" and "Sue" were
examined by
Peter Larson.
In the summer of 2000, Jack Horner
discovered five
Tyrannosaurus
skeletons near the Fort Peck Reservoir in Montana. One of the specimens,
dubbed "C. rex," was reported to be perhaps the largest
Tyrannosaurus
ever found.
In 2001, a 50% complete skeleton of
a juvenile
Tyrannosaurus was
discovered in the Hell Creek Formation in Montana, by a crew from the
Burpee Museum of Natural History
of
Rockford,
Illinois. Dubbed "Jane,"
the find was initially considered the first known skeleton of the pygmy
tyrannosaurid
Nanotyrannus but
subsequent research has revealed that it is more likely a juvenile
Tyrannosaurus. It is the most complete and best
preserved juvenile example known to date. Jane has been examined by
Jack Horner, Pete
Larson,
Robert Bakker,
Greg Erickson, and
several other renowned
paleontologists,
because of the uniqueness of her age. "Jane" is currently on exhibit at the
Burpee Museum of Natural History in Rockford, Illinois.
In a press release on 7 April 2006,
Montana State University revealed that it possessed the largest
Tyrannosaurus skull yet discovered. Discovered
in the 1960s and only recently reconstructed, the skull measures 59 inches
(150 cm) long compared to the 55.4 inches (141 cm) of "Sue's" skull, a
difference of 6.5%.
For a complete listing of discoveries,
see
Specimens of Tyrannosaurus
(external link).
Soft Tissue
In the March 2005 issue of
Science,
Mary Higby Schweitzer
of
North Carolina State University
and colleagues announced the recovery of soft tissue from the marrow cavity
of a fossilized leg bone, from a 68-million-year-old
Tyrannosaurus. The bone had been intentionally,
though reluctantly, broken for shipping and then not preserved in the normal
manner, specifically because Schweitzer was hoping to test it for soft
tissue. Designated as the Museum of the Rockies specimen 1125, or MOR 1125,
the dinosaur was previously excavated from the
Hell Creek Formation.
Flexible, bifurcating
blood vessels and
fibrous but elastic
bone matrix tissue were
recognized. In addition, microstructures resembling
blood cells were found
inside the matrix and vessels. The structures bear resemblance to
ostrich
blood cells and vessels. Whether an unknown process, distinct from normal
fossilization, preserved the material, or the material is original, the
researchers do not know, and they are careful not to make any claims about
preservation. If it is found to be original material, any surviving proteins
may be used as a means of indirectly guessing some of the DNA content of the
dinosaurs involved, because each protein is typically created by a specific
gene. The absence of previous finds may merely be the result of people
assuming preserved tissue was impossible, therefore simply not looking.
Since the first, two more tyrannosaurs and a hadrosaur have also been found
to have such tissue-like structures. Research on some of the tissues
involved has suggested that birds are closer relatives to tyrannosaurs than
other modern animals.
In studies reported in the journal
Science in April
2007, Asara and colleagues concluded that seven traces of collagen
proteins detected in purified
Tyrannosaurus rex
bone most closely match those reported in
chickens, followed by
frogs and newts. The discovery of proteins from a creature tens of millions
of years old, along with similar traces the team found in a mastodon bone at
least 160,000 years old, upends the conventional view of fossils and may
shift paleontologists' focus from bone hunting to biochemistry. Until these
finds, most scientists presumed that fossilization replaced all living
tissue with inert minerals. Paleontologist Hans Larsson of McGill University
in Montreal, who was not part of the studies, called the finds "a
milestone", and suggested that dinosaurs could "enter the field of molecular
biology and really slingshot paleontology into the modern world."
Subsequent studies in April 2008
confirmed the close connection of
Tyrannosaurus rex
to modern birds. Postdoctoral biology researcher Chris Organ at
Harvard University
announced, "With more data, they would probably be able to place
T. rex on the evolutionary tree between
alligators and chickens
and
ostriches." Co-author
John M. Asara added, "We also show that it groups better with birds than
modern reptiles, such as alligators and green anole lizards."
The presumed soft tissue was called
into question by Thomas Kaye of the
University of Washington
and his co-authors in 2008. They contend that what was really inside the
tyrannosaur bone was slimy
biofilm
created by bacteria that coated the voids once occupied by blood vessels and
cells. The researchers found that what previously had been identified as
remnants of blood cells, because of the presence of iron, were actually
framboids, microscopic
mineral spheres bearing iron. They found similar spheres in a variety of
other fossils from various periods, including an
ammonite. In the
ammonite they found the spheres in a place where the iron they contain could
not have had any relationship to the presence of blood.
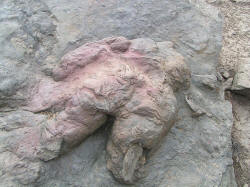
Footprints
Two isolated fossilized
footprints have been
tentatively assigned to
Tyrannosaurus rex. The first was discovered at
Philmont Scout Ranch,
New Mexico, in 1983 by
American geologist Charles Pillmore. Originally thought to belong to a
hadrosaurid,
examination of the footprint revealed a large 'heel' unknown in
ornithopod dinosaur
tracks, and traces of what may have been a
hallux, the
dewclaw-like fourth digit of the tyrannosaur foot. The footprint was
published as the
ichnogenus
Tyrannosauripus pillmorei in 1994, by
Martin Lockley and
Adrian Hunt. Lockley and Hunt suggested that it was very likely the track
was made by a
Tyrannosaurus rex,
which would make it the first known footprint from this species. The track
was made in what was once a vegetated wetland mud flat. It measures
83 centimeters (33 in) long by 71 centimeters (28 in) wide.
A second footprint that may have
been made by a
Tyrannosaurus was
first reported in 2007 by British paleontologist Phil Manning, from the
Hell Creek Formation of
Montana. This second
track measures 76 centimeters (30 in) long, shorter than the track described
by Lockley and Hunt. Whether or not the track was made by
Tyrannosaurus is
unclear, though
Tyrannosaurus and
Nanotyrannus are
the only large theropods known to have existed in the Hell Creek Formation.
Further study of the track (a full description has not yet been published)
will compare the Montana track with the one found in New Mexico.
Return to the
Old Earth Ministries Online Dinosaur
Curriculum homepage.

Tyrannosaur Shopping
Many fine reproductions
of Tyrannosaur teeth, claws, skulls, and even complete skeletons, are
available from several companies. Please click the links below to
visit their websites.
Bay
State Replicas - T-rex teeth, claws, skulls, jaws, foot, rib, femur,
complete skeleton (1/20 scale), brain cavity
Black
Hills Institute - Full size skulls, skeletons, 1/6th scale
disartictulated skull, teeth, arm, leg, femur, foot, claws.
Wall-mounted half-skull.
|