Old Earth Ministries Online Geology Curriculum© Old Earth Ministries (We Believe in an Old Earth...and God!) About Old Earth Ministries NOTE: If you found this page through a search engine, please visit the intro page first.
|
|
Geology - Chapter 5: Igneous RocksIgneous rocks form from a cooling solution of magma. They can form either underground or aboveground, and are said to be high-temperature rocks due to their high melting point. Because magma is rich in silica, most igneous rocks are silicates. To properly understand these types of rocks, one must first have a basic understanding of the nature of magma. |
Lesson Plan
Monday - Read Text Tuesday - Reading and Research Wednesday - Quiz Thursday - Review Friday - Test |
|
Parents Information
This lesson plan is designed
so that your child can complete the chapter in five days. This lesson
differs from the previous lessons in that there is also a reading assignment
on Tuesday. The only decisions you will need to make will be
concerning the research task for Tuesday. It is up to you to determine
if the student will simply fill in the answers, or provide a short essay
answer. You will also need to determine the percentage that this
research will play in the overall chapter grade, if any. |
|
|
Magma Magma is a complex mixture of liquid, solid, and gas. The main elements in magma are oxygen (O), silicon (Si), aluminum (Al), calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), potassium (K), iron (Fe), and magnesium (Mg). However, it is two major molecules found in magma that controls the properties of the magma. These two molecules are silica (SiO2) and water (H2O). Silica comprises as much as 75 percent of the magma. When rock melts deep underground, the magma rises through the earth's crust because the molten rock is less dense than solid rock. In many cases, the magma is unable to reach the surface, and it will cool in place many miles under the ground. This underground cooling produces the largest crystal sizes, because it cools more slowly. Sometimes the magma extrudes onto the surface, either on land or underwater. Magma which comes to the surface is called lava. Much of the magma that rises from the mantle comes from subduction zones, where oceanic crust dives beneath continental crust. Magma also rises to the surface under what is known as "hot spots." These are areas of volcanic activity that are not related to subduction zones. Current well-known hotspots include the Hawaiian Island chain and Yellowstone National Park. Types of Magma There are two basic types of magma which form in distinct tectonic environments. Basaltic magma (also known as "mafic") is created from the partial melting of the mantle, and it extrudes along rift valleys associated with ocean spreading centers. Popular belief says that magma originates deep within the earth's core, but this is not the case. The magma originates from the partial melting of material at a depth of no greater than 125 miles (200 kilometers). The other type of magma is granitic magma, which is commonly referred to as felsic magma. They are generated by subduction zones by the partial melting of oceanic crust as it dives underneath continental crust. Not all magma is a complete liquid. As the temperature rises, the minerals which comprise a body of rock each have their own melting point. Thus, the body of magma moving toward the surface could contain molten rock and crystalized minerals. This principle is known as partial melting. Another key term to understand is magmatic differentiation. When a magma cools, some of the crystallized minerals may be left behind as the rest of the magma continues on its journey to the surface. In other words, the magma sorts itself out according to the melting point of its constituent minerals. Rock Textures The texture of a rock refers to the individual mineral grains size, shape, and arrangement. There are six textures for igneous rocks.
1. Glassy Texture. Glassy texture is typical of volcanic material that cools instantaneously. The rock displays conchoidal fracturing with sharp edges like broken glass. No individual crystals can be seen. The picture at right shows a rock known as obsidian.
2.
Aphanitic Texture. Aphanitic texture consists of
extremely small crystals, and
3. Phaneritic Texture. A rock with phaneritic texture has crystal grains large enough to be distinguished with the eye. Granite is a typical phaneritic textured rock. 4. Porphyritic Texture.
In some rocks, larger crystals are embedded in rocks that otherwise would
appear to be aphanitic. The aphanitic portion of the rock is referred
to as the "matrix"
or "groundmass." 5. Pyroclastic Texture.
Pyroclastic textures refer to rocks which are blown out into 6. Vesicular Texture.
This texture appears in some texts, but not all. Vesicles are Several websites have good descriptions of igneous rock texture. Check them out if you wish to learn more. The first is Igneous Rock Textures, and the second one showing igneous rock formation with animations is here (click "Formation"). Classifiying Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks are classified based on their texture and composition. Thus, rocks are classified based on their cooling history (texture) and on the nature of the magma (felsic or mafic). A simple diagram for classification would be...
Another way to think of texture is by the location of cooling. Rocks which are glassy and vesicular are extrusive rocks. They were formed when the magma was extruded at the earth's surface. Aphanitic and phaneritic rocks are considered intrusive, or crystallizing from a melt below the earth's surface. (For advanced study: a QAPF diagram is also used to classify igneous rocks. To learn about it, click here.) (HINT: The chart above may be a good one to memorize!)
Individual Rocks
Below is a table of the rocks in the chart above. Click the name of the rock to view an external link with more information. Click the pictures for larger views.
End of Chapter Tuesday - Reading and Research In order to properly understand igneous rocks, one must understand the environment where they solidified. There are two main environments that we need to examine. First, extrusive rock bodies are rocks which have extruded onto the surface of the earth and solidified. Instead of discussing extrusive rocks here, we will cover it in the chapter on volcanoes. The second environment that we will consider here is intrusive rock bodies. Intrusive rock bodies are masses of magma which have cooled and crystallized below the earth's surface. We cannot observe this process, nor how long it takes. Many old geology texts had mere guesses at how long a large granite body took to cool, and they usually said millions of years. Young earth creationists have long argued that it can happen much quicker, and have written many articles in favor of rapid cooling. Thanks to recent advances in computer modeling and also in techniques such as Thermochronometry, geologists can calculate ages for cooling, all of which confirm that it does take millions of years to cool. There are several
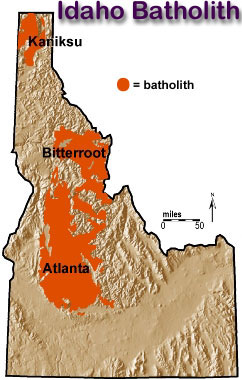
distinctive rock formations that are formed from intrusive igneous rocks. 1. Batholiths. Batholiths
are very large bodies of crystalline rocks, typically composed of granite.
They are the largest rock bodies in the earth's crust, and they can cover
several thousand square kilometers. For example, the
Idaho batholith is a large body of granite exposed over an area of over
40,000 square kilometers. It is unknown how deep under the surface
that batholiths
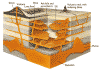
2. Stocks. Stocks are essentially small batholiths, less than 100 square kilometers. Stocks are important because many deposits of silver, gold, and other metals have been found in veins extending from a stock into the surrounding rock. 3. Dikes. A dike is
a narrow, tabular body of igneous rock. It forms where magma 4.
Sills. A sill is a tabular intrusive layer of rock that
is parallel, or concordant to, Sills commonly have inclusions, which are blocks and pieces of the surrounding rocks embedded in the igneous material of the sill.
5. Laccolith. A laccolith is an intrusive rock body that begins as a sill, as material fills in between rock layers. Because of the pressure, some sills can arch up the overlying sediments, creating a lens-shaped rock body, with a flat bottom, but curved at the top. Laccoliths tend to form at shallow depths.
End of Reading
Research
Research the answers to the following questions about intrusive body cooling. Your parents may have you simply answer the questions, or they may have you put it in essay form. Please follow your parents instructions. To answer these questions, utilize a search engine to locate the best webpages, or consult a textbook/encyclopedia. You may also use the links at the bottom of this page.
Today you will complete an 11 question practice quiz. The link to the quiz will open a new window. You can come back here and check your answers. Do not click the Back button on your browser during the quiz. After the quiz, continue your research project, if necessary. Please review the terms in bold in the text, and ensure you have completed your research work from Tuesday. Today you will take the end of chapter test. Please close all other browser windows, and click on the link below. During the test, do not click on the Back button on your browser. After you have completed the test, you may proceed to the next chapter on your next school day. Please return to the introduction page for the link to the next chapter. Return to the Old Earth Ministries Online Geology Curriculum homepage. Helpful Links
Stone Mountain, Georgia (Wikipedia) Stone Mountain, Georgia (Virtual Field Trip)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||